For lexical analysis , we can consider the input source program as a long sequence of characters with two pointers: a current pointer and a lookahead pointer.
When lexical analysis begins to find the next token, current and lookahead both point to the same character:
In the algorithm , four actions will be performed on these pointers:
1.GetChar : Moves the lookahead pointer ahead one character and returns.
2.Retract : Moves the lookahead pointer back one character.
3.Accept : Moves the current pointer ahead to the lookahead pointer.
4.Return : Returns a token consisting of a class and value , as well as performs any actions associated with that state , e.g., installing an identifier into the name table.
The driver program scans the input program and consults the entry at Table[State,InputChar] for the new state. The entry at Table[State,InputChar] consists of a new state and perhaps an action to be performed before moving to the new state:
Algorithm : Driver for Lexical Analysis
WHILE there is more input
InputChar := GetChar
State := Table[0,InputChar]
WHILE State <> Blank
InputChar := GetChar
State := Table[State,InputChar]
ENDWHILE
Retract
Accept
Return token = (Class,Value)
ENDWHILE
In the algorithm for the lexical analysis driver , retract is neccessary when a token is found because the algorithm will have scanned one character too far.




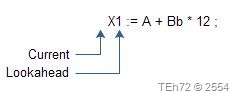

ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น